Do you understand the distinctions between a generator and an inverter and which one should be used in your specific application? The issue of Generator vs Inverter will be discussed here.
Are you curious in the functions of a generator? Linquip has information on how generators work and what they’re used for.
Are you looking for a location to buy Generator Equipment? Visit Linquip’s Generator For Sale to discover a comprehensive list of all Generator Products based on your requirements and application.
Linquip also supplies you with a list of Generator Suppliers and Companies from which you may choose the finest one.
Linquip offers a large number of Generator Manufacturers that can assist you in finding the perfect equipment for your needs.
The top Generator Service Provider companies can also take care of your industrial equipment services, such as installation, maintenance, and repair.
An inverter changes one kind of electrical current to another, while a generator generates electricity.
This is the most important factor to consider when deciding between a generator and an inverter.
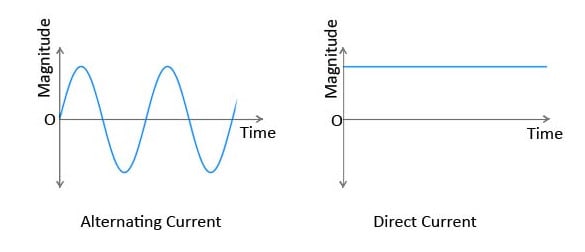
Electrical current is divided into two types: alternating (AC) and direct (DC) (DC).
When AC-powered gadgets must be operated in a vehicle or another location where only DC power is available, inverters are employed.
Although inverter generators may do both tasks for increased energy efficiency, the two units serve separate purposes.
“Inverters function differently from generators, they became popular in recent years since they create clean AC energy, they are quieter, and they do not make noise,” said a representative from 2nd city gas plumbing and heating, which specializes in boiler repair Redditch.
Inverters’ key benefit is that they create very high-quality, steady power output.
The drawback of inverters is also self-evident: they are rather costly.
Generators, on the other hand, must spin at a steady speed of about 3600 rpm in order to generate power.
Their biggest drawback is that they are quite loud, but they are cheap.”
What Is the Distinction Between AC and DC Currents?
The difference between alternating current and direct current is that in AC, electrons move back and forth, but in DC, electrons only flow in one direction.
AC loses less energy over long distances because it can withstand higher voltages.
As a consequence, AC is commonly used to provide electricity to most homes and structures.
As a result, most household appliances work on AC; nevertheless, to power the gadget, the AC electricity supplied to the building or home must be converted to DC.
Personal computers usually operate on DC and include a rectifier to convert the voltage.
The rectifier is more often referred to as a power supply in this scenario.
What is an Inverter and How Does It Work?
An inverter converts existing direct current electricity into alternating current electricity.
It does this by directing electricity via switches that send it in different ways.
The wave may then be smoothed down and given a steady frequency by using filters.
Because of their compactness and efficiency, power inverters have become quite popular in recent years.
Depending on how smooth the output has to be, different kinds of inverters utilize different filtering processes.
A device known as a rectifier is used to convert AC electricity into DC.
One of the most common applications of inverters is to generate electricity for various electronics in vehicles.
Cars often generate DC, which is incompatible with most gadgets designed to plug into standard residential outlets.
A tiny inverter may be inserted into an accessory port in most contemporary automobiles, allowing a cell phone, small TV, or other electrical devices to utilise the electricity.
Some inverters are designed to be connected into a car’s cigarette lighter.
On construction sites, larger inverters are used to provide energy for power tools and other equipment.
Inverters are used by solar and wind energy producers to convert the electricity they generate into a form that can be used in a house.
An important distinction between an inverter and a generator is that an inverter can only work if there is already a supply of electrical energy; it cannot generate its own.
Inverters only convert DC to AC unless they’re part of a combination machine, but a standard generator can’t alter the current from one form to another.
To learn how an inverter works, watch this entertaining video.

What Is The Procedure For Using A Generator?
A generator is a machine that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy.
Electric generators can usually provide all of the energy that a residence need.
Natural gas, coal, or nuclear energy may all be used to power large-scale electrical generators.
During a power outage, a portable generator typically burns gasoline or diesel fuel to create electricity for use on a construction site or building.
Generators may create either AC or DC energy, while the majority of generators used in power plants and smaller applications produce AC.
Traditional generators only accomplish this, despite the fact that they create energy.
A transformer, for example, is required if the voltage of electricity has to be switched.

See how a generator works in this fantastic video.
Generators with Inverters
Inverter generators work similarly to conventional generators in that they create AC electricity before converting it to DC and then back to AC.
This results in a more consistent, smoother flow of electricity.
The change also allows the generator to be more fuel-efficient and quieter than conventional types.
Converters of Energy
Some people mix up an inverter with a power converter, even using the names interchangeably.
To alter the voltage from one level to another, a converter is used.
Different nations use different voltage levels, thus tourists visiting other regions of the globe may need a converter to operate products like electric shavers and hair dryers.
Inverter vs. Generator
After going through the differences between generators and inverters, it’s time to discuss Generator vs Inverter.
There are far too many factors to consider if you want the greatest power backup to help you the most.
The key distinctions between a generator and an inverter are listed below to assist you decide which one to use:
The Difference Between a Generator and an Inverter
A generator is an electrical unit that provides emergency power for heavy power or household supply.
A generator is essentially a device that converts mechanical energy from outside sources into electrical energy.
During the power outage, it is largely used for electrical power distribution.
An inverter, on the other hand, is an electrical device that converts direct current from solar panels, batteries, or fuel cells to alternating power.
It’s a little gadget that connects to a battery or a pair of batteries that may be used to power common home equipment.
#1. Generator vs. Inverter Power Sources
The engine is the principal source of mechanical energy in a generator, and it usually runs on propane or gasoline.
Larger engines for industrial uses, on the other hand, run on natural gas, diesel, or propane.
Gasoline is one of the most common fuels for tiny generators, since it allows them to be more portable.
An inverter, on the other hand, converts stored energy into a conventional current.
Because AC is better suited for long-distance transmission, a grid-connected inverter transforms electricity from solar panels and wind turbines into AC main power.
#2. Generator Capacity vs. Inverter Capacity
Generators are large electrical devices that can bear huge loads and come in a variety of sizes.
They are useful in areas where there are frequent power outages and are more sophisticated when it comes to high power surges.
If the power spike is minor, it continues to run.
Nonetheless, starting a generator takes some time and effort.
Inverters are medium-capacity devices that are appropriate for usage in the home since they have less power spikes.
It has auto-shut capabilities that turn off the power in the event of rapid power surges, preventing harm to the device.
Inverters also start automatically when the electricity is turned off.
#3. Generator Maintenance vs. Inverter Maintenance
The majority of engine-powered generators run on gasoline or diesel, which needs routine maintenance such as oil changes, distilled water changes, and lubricating oil changes, among other things.
With proper management, gasoline and diesel have a shelf life of 12 to 24 months.
Furthermore, unless a fuel-stabilizing agent is used, gasoline cannot be deposited in substantial volumes for more than a few months.
Generators also emit additional noise.
Inverters, on the other hand, need little to no maintenance since they use simple circuitry to convert DC to AC.
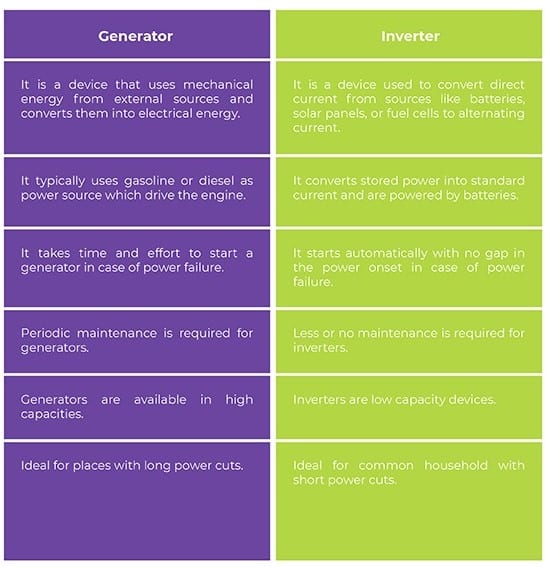
Chart of Comparisons
Here is a table that summarizes the key distinctions between generators and inverters:
Which Is The Better Option? Is It Better To Use A Generator Or An Inverter?
Inverter generators are more efficient than other kinds of generators because of the way AC current is produced, even though they produce less power.
The more efficient a generator is, the smaller the fuel tank and the less gasoline it consumes.
Generator vs. Inverter PDF Download
Look at this PDF for a better knowledge of the fundamentals of generators, their operating concept, and types.
Conclusion
Although generators and inverters are the two most often used technologies in the power generating business to decrease energy deregulation, their purpose and capability differ greatly.
Inverter generators are quite widespread these days, and they employ the same technology as the above-mentioned technology.
Inverter generators, on the other hand, vary from ordinary generators in that they create AC power, convert it to DC, and then convert it back to AC electricity.
This method offers several benefits in terms of power quality, fuel usage, noise output, and other factors.
Generators are complex, heavy-duty machines with vast capacity that take mechanical energy from outside sources, convert it to electrical energy, and then create electricity.
Inverters are low-power accessories that receive electricity from a fixed DC source and convert it to AC power using a microcontroller.
All contemporary domestic equipment, such as televisions, lights, and refrigerators, may be powered by inverters.
Diesel, gasoline, and propane are all common fuels for generators.